Chromomycosis
Chromomycosis /tropical blastomycosis, black chromoblastomycosis/ – chronic fungal infection related to deep mycoses. The disease is characterized by involvement of the skin and subcutaneous fatty tissue and the appearance of wart-like growths on them.
The internal organs can also be involved in the pathological process – liver, brain, bones. The causative agents of the infection form the specific pigment melanin, which colors the growths of the fungus in a dark color.
The disease is widespread, but most often occurs in countries located in tropical and subtropical climate regions, where warm and humid weather prevails and where the average annual temperature varies between 12-24 degrees Celsius and the annual amount of precipitation is average about 2500 mm.
These are the southern parts of North America, Mexico, the countries of the Caribbean, the northern and southern parts of Africa, the southern part of Europe /Spain, Italy/ etc.
Most often, the disease occurs in males between the ages of 20 and 60.
Prognosis with correctly selected and timely treatment is favorable, but the disease takes a very long time and is characterized by frequent relapses /resumption of the disease/.
What are the causes?
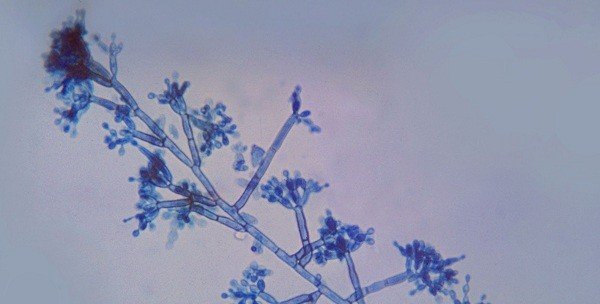
The cause of this infectious disease is the fungus of the De-matiaceae family: Fonsecaea pedrosoi /the most common/.
Fungi are dimorphic by nature, that is, they occur in 2 forms:
• Their tissue form looks like oval or round cells of light brown or brownish color with a diameter of 10-12 microns.
• The mycelial form is represented by thin threads of olive green color.
The causes of the disease are found on plants and in the soil. The infection occurs when the spores of the fungus fall on the skin in areas where its integrity is broken, such as cuts, abrasions, abrasions, scratches, etc.
The infection is not transmitted from an infected person to a healthy one.
Among the risk groups are:
• Agricultural workers;
• Miners;
• People residing in countries located in the subtropical, tropical, subequatorial and equatorial climate zones who walk barefoot and cultivate the land.
What are the symptoms?
Sufferers of this disease report:
• General fatigue;
• Rapid fatigue;
• Decreased appetite;
• Headache;
• Slight increase in body temperature – up to 37.5 degrees Celsius at most ;
A lesion on the skin occurs a few days after the fungus falls on it. Most often, the process is localized on the skin of the lower and upper extremities. A red or reddish papule appears on the skin.
A few months later, together with this papule, wart-like growths of brown or red color, which look like cauliflower, begin to form. Gradually, the foci of infection on the skin merge, forming large areas with a diameter of up to 20 cm.
Treatment of chromomycosis
Therapy begins with intravenous administration of antifungal preparations, most often amphotericin B – 0.5-1 mg per kilogram of body weight once a day.
Subsequently, the treatment continues with the oral administration of anti-fungal medications, and the skin lesions are treated locally with suitable ointments for this purpose.
Most suitable for this infection are considered:
Pills
• Itraconazole 200-600 mg daily;
• Ketoconazole – 400-800 mg every 24 hours;
Duration of therapy is determined individually by the attending physician.
Along with antifungal agents, skin lesions are treated with vitamin D and iodine. Small lesions are subject to surgical removal.
What are the complications?
• Cosmetic defects on the skin;
• With a severe inflammatory process, there is a possibility of the occurrence of squamous cell carcinoma.



