Trichocephalosis
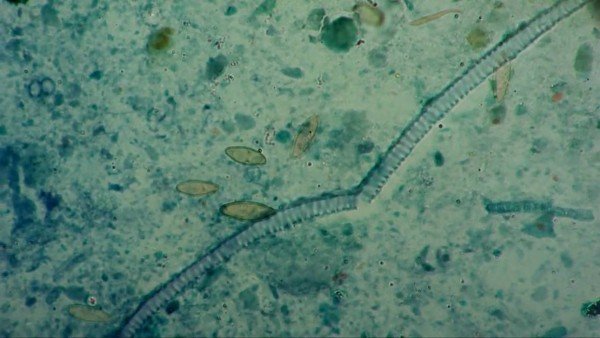
Description
Trichocephalosis is parasitism, which is caused by the parasitic organism Trichocephallus trichiuris, better known as cosmocephalus. In our country, this nematode is more -widespread in mountainous and higher altitude areas, as well as in forested areas.
The earthworm has a whitish-colored body with a thin, thread-like elongated front end, this end being 2/3 of the length of the roundworm. The back of the parasite is thick and short. In males, the rear part is spirally twisted, and in females, the rear end is bent like a saber.
Life cycle of the helminth
The main host of the parasite is man. Sexually mature specimens usually inhabit the cecum /caecum/ and the ascending part of the large intestine. The worm attaches itself to the host’s intestine by its pointed front end /not with the fringes, but with the mouth/.
Penetrates into the mucosa, submucosal layer and muscle layer of the intestinal wall and begins to feed on the juice of the tissue and less often on the blood of its host. In this case, the posterior part of the parasite remains free in the lumen of the intestine.
After fertilization, the female lays from one thousand to 3,500 eggs per day. Together with the feces, the eggs fall into the external environment, where they develop under the influence of oxygen and sufficient moisture. Invasive roundworm larvae which resemble a spear-shaped probe develop inside the mature egg.
Infection occurs by swallowing infected eggs. The eggs then hatch in the intestine and the larvae, thanks to their lance-shaped appendages, enter between the intestinal villi of the iubercuen glands and continue their further development for 3 to 10 days.
Subsequently, the larvae in the lumen of the intestine descend into the cecum. In this place, they reach sexual maturity after half a month. The life span of the helminth in the human body is about 7 years.
What are the symptoms?
The clinical picture of this parasitosis is quite diverse. This depends on the presence of concomitant diseases, reactivity of the body and intensity of infection.
If the infection is not intense the disease proceeds in a subclinical /pre-start form/. With a higher intensity of the parasitic process, symptoms of gastrointestinal and nervous pathology are usually manifested.
And as a result, characteristic clinical manifestations appear – loss of appetite, nausea, vomiting, drooling. There is also pain on the right side of the abdomen, similar to appendicitis, as well as spasmodic pains in the region of the epigastrium, reminiscent of peptic ulcer or gastritis.
Most affected develop diarrhoea, sometimes mucus in the stools and blood. Patients complain of headaches and dizziness, irritability, sleep disorders, and sometimes nausea and seizures.
A characteristic feature of the disease is that it does not have characteristic signs and pronounced symptoms, and the diagnosis requires qualified laboratory tests.
Treatment of trichocephalosis
Treatment is usually done on an outpatient basis based on the detected trichocephalus. However, there are cases of complications that require hospitalization. Medicines such as albendazole, mebendazole and carbendazole or flubendazole are used to destroy the parasite.
It should be noted that the choice of medicine takes into account the patient’s state of health and whether he has chronic diseases. After the completion of the therapy, probiotics and enzyme preparations are prescribed.
The first dose of mebendazole achieves 90% eradication of the parasites. Supplemental iron intake is required to resolve the iron deficiency in the blood caused by the roundworms and to heal the injured intestinal wall.



