Contagious mollusc
Description
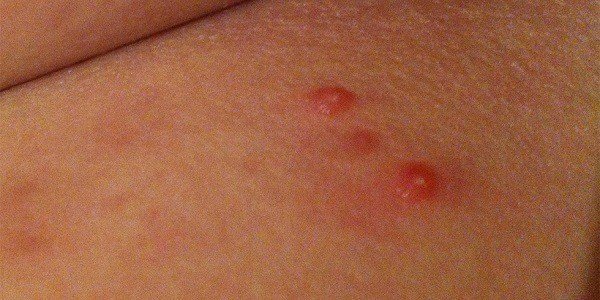
Mollus infection is a skin infection that is caused by a virus. It affects mainly children and young people. Characteristic of the skin infection is the appearance of skin lesions that resemble raised, rounded bumps with a white, pink or flesh-colored color.
The virus is transmitted through direct contact with an infected person or by touching infected objects. The infection is most often diagnosed by a dermatologist based on the characteristic appearance of the skin lesions, strong> although it is often necessary to histologically examine material from the lesions.
The disease is benign and self-limiting in healthy people and does not always require treatment. However, in some people, such as those with weakened immune systems, treatment is often required because skin lesions are more resistant and can spread to more places on the skin.
Maintaining good personal hygiene and avoiding direct contact with infected people can help prevent this type of viral skin infection.
What are the symptoms?
The rash starts as small painless papules – small raised lumps, each about 2-5 mm in diameter.
Lesions usually appear as dome-shaped papules, which have a waxy, smooth or pearly surface. They are white, pink, or flesh-colored, and over time a depression appears in their center that contains a thick, white, cheese-like substance. This core can be squeezed out easily. There may be redness and scaling of the edges of the lesions due to injury.
Lesions can appear in any area of the skin. They are usually clustered in one or two areas of the skin, but can be spread anywhere. In children, the rash appears on the face, torso and limbs, and in adults, the lesions are in the genital area, perineum and on their inner thighs. Usually the lesions are about 20 in number, but in some cases they can to reach several hundred.
The rash does not affect the palms or soles and in very rare cases lesions may appear on the mucous membrane of the mouth.
Usually there is no itching or tenderness to the touch and generalized symptoms such as fever, nausea or fatigue do not develop.
Treatment of molluscum contagiosum
In healthy people, because the disease is self-limiting, it usually resolves spontaneously after a few months. Once the diagnosis is made, the initial home treatment measures should be aimed at preventing the spread of the virus to other people.
You should also avoid scratching the lesions. This will prevent the possible spread of the virus to other parts of the skin and wounding of the skin, which can cause secondary bacterial infection due to the penetration of bacteria into the injured zones.
How to protect yourself?
Since the virus is transmitted by direct contact, try to avoid contact with the skin surface of infected people. Those affected should cover exposed your lesions with clothing or a bandage to reduce the chance of transmission. There is no need to stop sick children from school.
Avoid sharing personal items such as towels, compresses, clothing and razors.
Avoid contact with potentially infected objects such as fitness equipment, mats and benches.
Since the rash can spread from one part of the skin to another by touching the lesions, avoid scratching or squeezing the lesions.



