E. coli
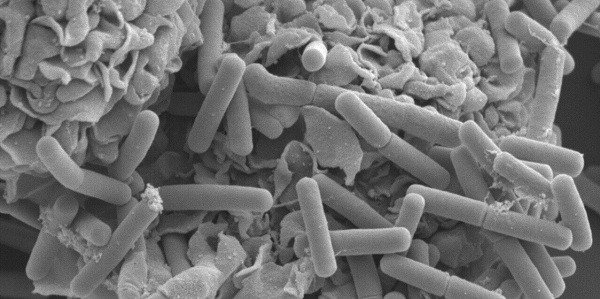
The bacterium Escherichia coli (E. coli) usually inhabits the intestines of healthy people and animals. Most types of E. Coli are harmless to humans or cause brief diarrhea.
A particularly dangerous group of strains, such as E. coli O157:H7, can cause severe abdominal pain, bloody diarrhea and vomiting.
A person can come into contact with E. Coli from contaminated food or water, especially from poorly washed raw fruits or vegetables and undercooked beef.
Healthy adults usually recover from E. coli O157:H7 infection within 1 week, regardless of gender
But young children and the elderly are at increased risk of developing a life-threatening form of kidney failure called hemolytic uremic syndrome.
A dangerous strain of Escherichia coli – how to protect yourself
What are the symptoms
Clinical manifestations of E. coli O157:H7 infection usually begin in 3 or 4 days after exposure to the bacteria. It is possible for a person to get sick immediately, about a day after the exposure or a week later, and the identification of the infection with the dangerous strain takes place only after an examination, most often of urine.
The most common manifestations of the bacterial infection are:
- Diarrhea, which can be of varying degrees of intensity and characterized by watery or bloody stools.
- Abdominal cramps, pain and increased sensitivity to touch and pressure of the external abdominal wall;
- Characteristic symptoms in some cases are nausea and vomiting;
- There is also a danger of infection in the vaginal discharge.
It is necessary seek medical attention if diarrhea persists, bowel movements are too frequent or blood appears in the stool.
What are the causes
Of the many strains of E. Coli, only a few cause diarrhea.
However, one group of bacteria, which includes O157:H7, releases a strong toxin that damages the lining of the small intestine, possibly causing bloody diarrhea.
Infection develops after ingestion of the dangerous strain of E. Coli.
Unlike many other disease-causing bacteria, the dangerous strain of E. Coli is capable of causing infection, even after ingesting minimal amounts of it.
Deteriorating health from the bacteria and signs of developing infection are possible after eating just one slightly undercooked burger or swallowing one sip of contaminated pool water.
Potential sources of infection with this strain of bacteria are contaminated food or water, as well as direct contact with an infected person.
Infection with the dangerous strain of E. Coli develops from eating contaminated food such as:
Human and animal feces can contaminate groundwater and surface water, including streams, rivers, lakes and water used to irrigate crops on farms.
Although there are established standards for the treatment of drinking water with chlorine, ultraviolet light and ozone, which destroy almost all bacteria, some cases of infection may also be due to contamination of municipal drinking water, as the risk of to occur is greatest in small settlements, especially after heavy rainfall.
Bacteria can easily pass from one person to another, especially if the uninfected person does not wash their hands properly.
Escherichia coli treatment
Supportive therapy is applied. The patient is advised to rest and drink more fluids. If the severe form of kidney failure develops as a complication of the infection, hospitalization is required. In most cases, it is not necessary to prescribe antibiotics.
How to prevent the danger of the insidious strain of Escherichia coli
To prevent infection, it is necessary to observe control measures at all stages of the food chain – from the production of agricultural products on farms to processing, < strong>processing and preparation of food products both in commercial enterprises and at home.
In industrial conditions
The number of cases of the disease can be reduced by carrying out various measures during the production of minced meat. For example, animals are examined before slaughter to prevent a large amount of pathogenic bacteria from entering slaughterhouses.
Appropriate measures that are observed in slaughterhouses and compliance with hygiene reduce the risk of contamination of meat with feces, but do not guarantee the absence of dangerous Escherichia coli in the food.
To minimize the likelihood of microbiological contamination, it is extremely important that farm workers and slaughterhouse workers maintain sufficiently good hygiene.
The same applies to the employees of the enterprises in which they produce meat food products. The most careful should be with sausages and meat delicacies.
The only effective way to destroy the dangerous strain of intestinal bacteria in food products is bactericidal treatment – heating, for example, heat treatment or pasteurization, or irradiation.
At home
Measures for the prevention of infection with the dangerous strain of Escherichia coli are similar to the measures for the prevention of foodborne diseases.
5 are the main principles that can ensure that no infection with the dangerous bacteria that can lead to the development of kidney failure occurs.
1. Observance of hygiene
Hands must be washed before contact with foodstuffs. This should also be done frequently when preparing food.
A leading recommendation that even small children know – to wash their hands before going to the toilet.
Wash and disinfect any surfaces and kitchen utensils used in food preparation.
It is necessary to take measures to protect the kitchen from insects, rodents and other animals.
2. Separate the raw products from the thermally processed
Separate raw meat, chicken and seafood from other foods. To process raw products use different kitchen utensils and accessories – different knives and kitchen boards.
3. Good heat treatment of food
Meat, chicken, eggs and seafood should be well-heated.
It is good to let the soups boil, to make sure that the temperature during their preparation will reach 70 degrees. Remember that the juice of the finished meat or chicken should be light, not pink in color. Use a thermometer if possible. Reheat ready-made food well.
4.Store food products at a safe temperature
- Do not leave ready-made food at room temperature for more than 2 hours;
- The cooling of all perishable foods should not be delayed – preferably to a temperature below 5 degrees;
- Do not store food for too long, even in the refrigerator;
- Do not defrost food at room temperature.
< li>Keep ready meals hot – above 60 degrees until they are served;
5.Use safe water and safe raw products
- Use clean water when cooking or purify it;
- Choose fresh and healthy products;
- Do not use products after their expiration date.
Raw products, as well as water and ice, may contain dangerous microorganisms, including the Escherichia coli strain that can cause kidney failure.
Toxins can form in spoiled or moldy food products. Carefully selected and well-washed food products are safer for health.



