Herpangina
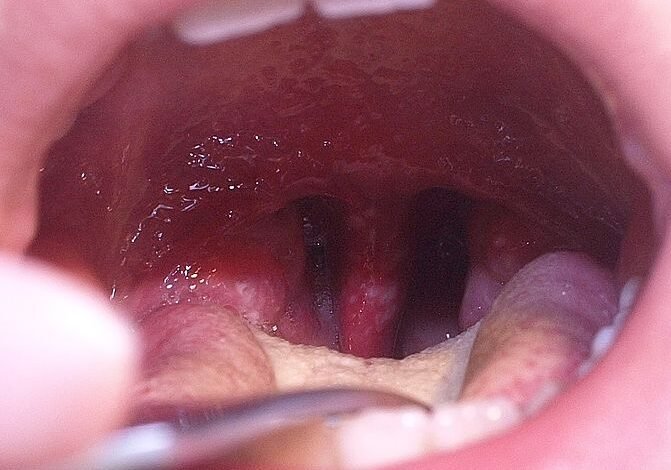
Herpangina – this is a common childhood disease, sometimes , which causes fever and is characterized by the appearance of transparent bubbles that turn into ulcers on the soft palate and back of the throat.
The clinical condition is very similar to hand, foot, mouth disease. It is caused by enteroviruses that are passed from person to person and you should be aware that complications in children are common.
It is characteristic of these viruses that they multiply in the digestive tract, but are released into the environment with feces, so the fecal-oral mode of infection is the main one.
The disease manifests itself most often between the ages of 1 and 4, and it occurs mainly in closed groups – nurseries, kindergartens, preschools, where children have close contacts and stay in one room for a long time.
The main cause of herpangina is the Coxsackie virus most often. It is characterized by a high contagion index and infection becomes more than easy. Treatment is easy, and as long as you watch for complications, you can expect a full recovery within a week.
What are the symptoms of herpangina
- Sudden rise in body temperature;
- Sore throat;
- Headache and neck pain;
- Loss of appetite;
- Dribbling – involuntary flow of saliva from the mouth in babies;
- Vomiting in babies.
The sores in the back of the mouth and throat begin to appear about 2 days after the initial symptoms appear. They are usually grayish in color and often the rash is surrounded by skin that is redder than the surrounding tissue. After prescribed treatment by a pediatrician, you can expect the sores to disappear in about a week.
Seek medical attention if you notice your child has the following symptoms:
- Very high temperature – 39-40 degrees Celsius, which you cannot bring down;
- Aphthae in the mouth or sore throat lasting more than 5 days;
- Symptoms of dehydration – dry mouth, child crying without tears, sleepiness, decreased frequency of urination, darker colored urine or sunken eyes.
Sores on the throat and back of the the mouth is characteristic only of this disease, therefore the diagnosis is made very easily with only a physical examination, without the need for other tests.
What are the causative agents
It is usually caused by coxsackievirus group A, but the infection can also be caused by coxsackievirus group B, enterovirus 71, and echo virus.
It is transmitted by the fecal-oral route, which means that the infection spreads through the entry into the mouth of a healthy person of fecal particles infected with the causative viruses. The causative viruses are highly contagious and spread easily among young children, especially in schools and kindergartens.
Treatment of herpangina
Treatment is based on various factors, such as the child’s age, specific symptoms, and his tolerance to certain medications. Antibiotics are not an effective remedy for viral infections. The main goal of treatment is to limit and control the symptoms.
Your doctor may recommend:
Preparations with the active ingredient Ibuprofen or Paracetamol of various pharmaceutical companies to relieve discomfort and reduce high temperature. Do not use aspirin to suppress the symptoms of a viral infection in children and adolescents, as it is possible to make them sick with Reye’s syndrome.
- Local anesthetics to relieve pain in the mouth, although these are usually not needed;
- Increase the child’s fluid intake – especially give him cold milk, cold water and ice creams a stick. Avoid citrus juices and drinks and hot ones, as they can make symptoms worse;
- While your child is recovering, you can feed him foods he likes, such as ice cream. Any cold dairy products are acceptable. Avoid giving him spicy, fried or sour foods;
- If the child feels severe discomfort and refuses to eat, you can offer him liquid food in the form of soups, purees and everything else that is soft. This way, the little ones will not have difficulty swallowing, which is the main reason they refuse to eat;
- The symptoms of herpangina usually disappear in about 7 days, with no lasting consequences for the health of the child.
Prevention is of great importance
It is quite possible to limit the risk of this disease. For this purpose, attention should be paid to maintaining high personal hygiene. This includes frequent hand washing, as well as regular ventilation of the rooms where the children are.
Until the time when the child is not completely healthy, he should not attend a kindergarten or nursery, so as not to transmit the infection.



