Pleurisy
Description
Pleuritis is a disease in which a membrane consisting of a layer of tissue that covers the inside of the chest and another layer of tissue that surrounds the lungs becomes inflamed .
It causes severe chest pain /pleural pain/ that worsens with breathing.
Multiple co-morbidities can cause pleurisy.
What are the symptoms?
Clinical manifestations of inflammation of the pleura can consist of:
• Chest pain occurs that worsens with breathing, coughing or sneezing;
• Shortness of breath as the sufferer unconsciously restricts their breathing in an attempt to reduce the pain.
• Only in some in some cases, a cough appears and those affected have a fever;
• The painful feeling in the chest can spread and cover the shoulder as well;
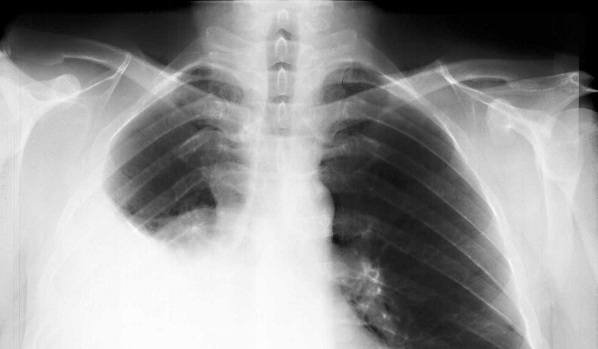
In some cases, fluid accumulates between the two tissue layers /pleural cavity/. The condition is referred to as pleural effusion.
When the amount of fluid is not much, the pleural pain decreases or disappears because the two layers of the pleura are no longer in contact.
But the large amount of fluid in the pleural cavity can create a pressure that is so great that it compresses the lung and it loses some or all of its function.
This makes breathing extremely difficult, and the large amount of fluid can become infected. This condition is referred to as empyema and may be accompanied by fever.
Call your GP straight away if you experience vague, severe chest pain when breathing.
You may have a problem with your lungs, heart or pleura, which requires prompt medical attention.
What are the causes?
Two large layers of tissue called the pleura separate the lungs from the chest wall. One layer wraps the respiratory organs on the outside, and the other the inner chest wall.
Between the 2 layers there is a small space called the pleural cavity, which is usually filled with a small amount of fluid.
The layers act like a satin, allowing them to slide over each other, which ensures the smooth contraction and expansion of the lungs during breathing.
Pleuritis develops when the pleura becomes irritated and inflamed.
As a result, the 2 layers of the pleural membrane begin to rub against each other like two pieces of sandpaper, causing pain when inhaling and exhaling.
Pleural pain diminishes or stops with breath holding.
The reasons for the development of pleurisy are:
• Viral infection, such as flu /influenza/;
• Bacterial infection such as pneumonia;
• Fungal infection;
• Rheumatoid disease such as rheumatoid arthritis;
• Certain medications;
• Malignant tumor formation of the lung near the pleura;
Treatment of Pleurisy
Treatment that is applied primarily focuses on the main cause of the inflammation of the pleura.
For example, if a bacterial infection is the cause, prescribing antibiotics will help control the infection. If the cause is a virus, the disease will subside by itself.
The outcome of treatment depends on the severity of the underlying disease. If the cause of inflammation of the pleura is detected in time and the therapy is started promptly, a complete cure is achieved.
To relieve symptoms, you can do the following:
• Start taking ibuprofen, which will help reduce pain and inflammation;
• Take a break and try to find which body position gives you the least pain and stay in that position as long as you can. Even if you feel better, refrain from making sudden movements.



