Sporotrichosis
Sporotrichosis is a skin infection caused by the fungus Sporothrix schenckii. This infectious organism is very similar to that found in stale bread or the yeast used to make beer.
Also, the fungus is most often found in the thorns of rose bushes, hay, peat moss, branches and soil.
Consequently, infection more often affects gardeners, farmers and generally people handling roses, moss, hay and soil. Sometimes animals such as dogs or horses can become infected.
The disease is often referred to by older authors as rose handler disease because its incidence was higher among people who lived near growing roses.
This is due to the fact that the fungus is most often on the thorns of the rose and in the fertilizer and soil that are used to cultivate these plants. And they easily penetrate the human skin through the wounds that rose thorns make.
What are the symptoms?
Once the fungal conidia /spores/ have penetrated the skin through wounds caused by thorns, scratches or otherwise, it may be necessary to several days to months for infectious organisms to cause infection.
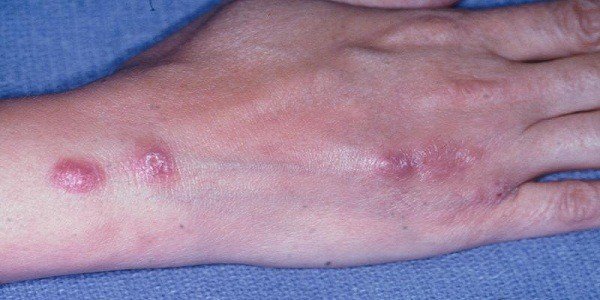
The first symptom is the appearance of a hard lump /nodule/, the color of which can vary from pink to almost purple. The nodule is usuallypainless and only mildly tender.
Over time, the bump may develop into an open sore /ulcer/ from which a clear fluid may ooze. In other cases, mycetomas may form.
Mycetomas are places where granules containing the organisms causing the infection leak from the lymph through the sinus tracts.
Untreated ulcers and nodules can become chronic and not change for years. In about 60% of cases, the fungus spreads to the lymph nodes.
Over time, new bumps appear on the infected arm or leg. This process can take years. In very rare cases, the infection can spread to other parts of the body.
The fungus can infect the joints, bones, lungs and tissues around the brain /fungal meningitis/. Fortunately, such a generalized fungal infection only develops in people with a suppressed immune system. But in these cases, the disease is life-threatening and very difficult to treat.
Symptoms are progressive. Initial sites of infection are not visible. As the infection progresses, lesions develop that are located successively along one line and the lymphatic channels become infected.
Treatment of sporotrichosis
Treatment depends on how far the fungus has spread in the infected person’s body and his general state of health.
• When the infection is only on the skin – they are traditionally treated with a saturated solution of potassium iodide and this medicine is applied 3 times a day for 3 to 6 months, until all lesions disappear. Skin infections can be treated with intraconazole for up to 6 months.
• Bone and joint infection – these are very difficult to treat and rarely respond to the action of potassium iodide. Intraconazole is often used to treat for several months or even up to 1 year.
The drug amphotericin is also administered, but it can only be taken intravenously. But this medicine has
more side effects and may need to be administered for many months.
• The literature also mentions alternative treatment methods – fungicidal herbs such as myrrh, tea tree oil, citrus seed extract, olive oil and garlic are applied directly to the infected skin. Although the effect of these herbs is only speculated, there are still several studies that confirm it.



