Blastocyst
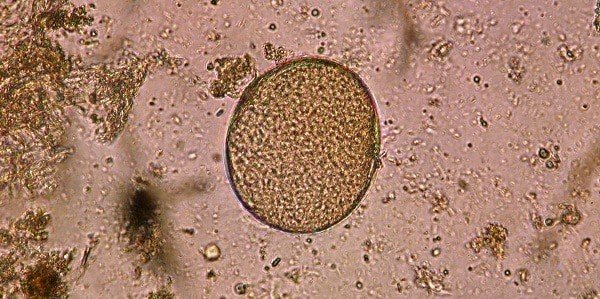
Blastocyst hominis is a microscopic parasite that is sometimes found in the feces of healthy people, as well as in the feces of those who have diarrhea, abdominal pain, or other gastrointestinal problems.
Infection with Blastocystis hominis is called blastocytosis.
Scientists are not yet fully aware of the function of Blastocystis hominis in causing infections and whether only certain subtypes of the parasite are infectious.
Certain subtypes of Blastocystis hominis have been shown to be more likely to lead to the development of symptomatic infection. In some cases, parasites live in the digestive tract without causing harm.
There are no officially approved treatments for blastocytosis, but fortunately the infection usually clears up on its own.
However, if signs and symptoms develop and do not improve over time, your doctor may prescribe some medications that may help.
What are the symptoms?
• Diarrhea;
• Nausea;
• Abdominal cramps;
• Bloating;
• Too much gas/flatulence/ ;
• Anal itching;
• Loss of appetite;
• Unexplained weight loss;
• Fatigue;
Seek medical attention if you have diarrhea or cramping that lasts longer than 3 days.
What are the causes?
The infectious organism was originally thought to be a harmless fungus, but Blastocystis hominis was later found to be a parasite, a microscopic single-celled organism /protozoan/.
Many protozoa inhabit the gastrointestinal tract and are harmless or even beneficial, while others cause disease.
Whether Blastocystis hominis is a type of disease-causing protozoa is controversial.
Although many people who carry this parasite do not develop any signs or symptoms, the microorganism is found in others who suffer from diarrhea and other gastrointestinal problems.
But since Blastocystis hominis is often found together with many other microorganisms, scientists wonder whether the blastocyst alone causes infection or is just harmlessly present in the affected area.
p>
It is also possible that some people carry Blastocystis hominis and show no signs or symptoms of disease, while others are more susceptible.
Many types of protozoa enter the gastrointestinal tract via the fecal-oral route, and the most common entry occurs when a person does not thoroughly wash their hands after using the toilet and before preparing food.
Scientists are not sure how Blastocystis hominis is transmitted, but it is believed to bethrough oral-fecal contact.
But it is known that blastocytosis occurs more often mainly in regions with low public hygiene and lack of hygiene habits among the population.
What are the complications?
In most cases of diarrhea due to Blastocystis infection, it is self-limiting.
However, with this condition, the body always loses vital fluids, salts and minerals, which can cause dehydration. Children are particularly vulnerable to dehydration.
Treatment of blastocyst
If the infection is without signs and symptoms, no treatment is needed. And the mild manifestations of blastocytosis disappear by themselves within a few days.
Potential drugs to treat Blastocystis infection are the antibiotic metronidazole, the combination of the drugs sulfamethoxazole and trimethoprim, and the antiprotozoal drugs iodiquinol or nitazoxadin.
However, it should be borne in mind that each organism reacts differently to the above-mentioned medications.
And since the symptoms the sufferer is experiencing may not be related to Blastocystis, it is possible that any improvements may be due to the action of the prescribed medication on another organism.



