Cytomegaly
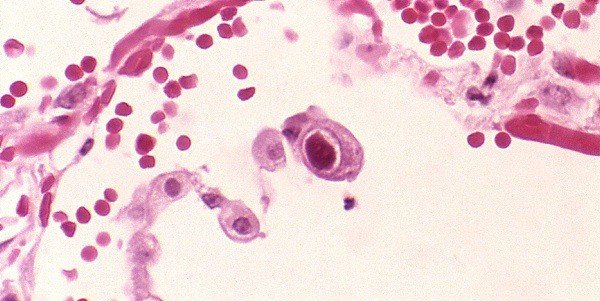
Cytomegaly is a viral disease that is caused by the cytomegalovirus, belonging to the genus human herpesvirus type 5. This virus is quite common, as antibodies against it are found in 10-15% of adolescents and in 40% of people in adulthood.
Recognizing the presence of cytomegalovirus is unfortunately not possible immediately. The disease that causes – cytomegaly or cytomegalovirus infection has a relatively long incubation period, about 60 days.
During this period, the viral infection may not manifest itself at all, but after that the symptoms almost certainly appear unexpectedly and in most cases can cause stress, hypothermia or a general weakening of the immune system.
Unfortunately, very often cytomegaly is confused with such diseases as colds and acute respiratory infections, since cytomegalovirus infection resembles these diseases in its symptoms.
The characteristic symptoms of cytomegaly are headache, general weakness, if the presence of cytomegalovirus infection is not detected in time, the consequences can be very serious, such as pneumonia, encephalitis, arthritis, etc.
Since this virus was discovered relatively recently, in 1956, it has not been well studied until now. In the scientific community, this virus is still the subject of heated debate. In fact, in medicine cytomegalovirus is the basis of many speculations.
Cytomegalovirus infection
Infection is possible through sexual contact through semen or through the mucus in the cervical canal, through saliva, breast milk and through blood. Infection of infants usually occurs during birth or during breastfeeding.
Older children can become infected from each other, most often this happens in nurseries and kindergartens, where they often put common toys in their mouths or, simply put, they get infected from saliva.
Adults, as stated, acquire the virus through kissing or sexual contact. It is necessary to note the fact that the cytomegalovirus is not very contagious, in the sense that in order to infect a person with it, it is necessary to be in prolonged contact with a sick person.
Cytomegalovirus is very common in humans. Antibodies against this virus are detected in 10-15% of adolescents. And in people aged 35 and over, cytomegalovirus is found in 50%.
What are the symptoms?
People with normal immunity may be infected with this herpes virus and not know it because their immune system would keep the infectious organism in a suppressed state, therefore there would be no infection to develop.
And the presence of the virus in the body would not cause harm. In rare cases in people with normal immunity, cytomegalovirus can cause a syndrome similar to mononucleosis.
This condition usually appears about 20-60 days after contracting the virus and lasts for 2 to 6 weeks. The manifestation of this syndrome consists in the occurrence of the following symptoms: chills, severe headache, general disposition.
In most cases, it ends successfully, with complete clinical recovery.
In people with weak and weakened immunity, namely HIV-positive, those suffering from oncological diseases, etc. cytomegalovirus causes severe diseases that affect the eyes, lungs, brain and digestive system, with a possible fatal outcome.
Treatment of cytomegaly
The therapeutic approach that is taken in this disease should be complex, applying parenteral leukocytic interferons for a period of 2 weeks.
In addition, therapy is prescribed to strengthen the immune system, vitamins, minerals and immunostimulators are prescribed.



